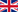
Grape Hyacints as Cutflower
 PRODUCING GRAPE HYACINTHS (as cut flowers)
PRODUCING GRAPE HYACINTHS (as cut flowers)
practical tips for
- arriving at a well-considered choice of cultivar and bulb size
- treating the bulbs properly before the production process
- providing the right horticultural practices to yield a compact plant for cut flower
- preventing problems throughout the production phase
Choice of right variety and proper planning are important
Varieties for producing cut flowers
Although there are several varieties of Grape Hyacinth, Muscari armeniacum and certain of its cultivars are the ones primarily used for producing cut flowers. Muscari latifolium, however, is also sometimes used. This manual focuses on the use of Muscari armeniacum.
Scheduling the bloom period
Muscari armeniacum can be forced into bloom from January through April. After lifting and drying, the bulbs are stored at 20°C, the temperature at which flower initiation occurs most quickly. For late-season bloom (March/April) the bulbs should be stored at 17°C from 1 October. A cold period lasting 15 to 16 weeks is necessary for proper flower production, but an extra week of cold is acceptable. Do not start the cold period before the end of August. Compared with other bulbous plants, flower initiation in grape hyacinths occurs a little later in the season. Starting the cold period too soon will prevent all the individual flowers in the inflorescence from being initiated. For forcing purposes, this will result in inflorescences with a white top and desiccated flowers. The earliest bloom will require at least 16 weeks of cold to produce good flowering results without flower desiccation while still keeping the number of days in the greenhouse to a minimum. Bulbs intended for flowering in February can be held a week less in cold storage and still produce good flowering results quickly. Until the cold period begins, store the bulbs under dry, ventilated conditions. If the RH is too high, fungal growth (caused by Penicillium or other fungi.) can appear on the bulbs. In the early stages, the symptoms caused by Penicillium will only result in a less attractive bulb. Eventually, however, the fungus can damage the bulb enough to keep it from growing properly.
Table 1. Cold treatment (both duration and temperatures) for each flowering period. The length of the housing period is based on a greenhouse temperature of 18°C.
| bloom date | cold treatment | start of cold treatment | housing period at 18°C |
| January | 16 wks. 9°C or 5 wks. 9°C + 11 wks. 5°C | End of August to mid-September | 3 - 3.5 weeks |
| February | 15 wks. 9°C or 4 wks. 9°C + 10 wks. 5°C | 2nd half of September to mid-October | 2.5 - 3 weeks |
| March | 15 wks. 9°C or 4 wks. 9°C + 10 wks. 5°C | 2nd half of October to mid-November | 2.5 - 3 weeks |
| April | 15 wks. 9°C or 4 wks. 9°C + 10 wks. 5°C | December | 2 - 2.5 weeks |
Prevent tall leaves by lowering cold treatment temperature or planting later
Using cold treatment to prevent tall leaves: should bulbs be stored dry or planted?
An important point to consider when forcing Muscari armeniacum is its leaf development. In some cases, the leaves can grow taller than the flowers, and this makes it difficult to harvest the flowers. When the bulbs are planted before they go into cold treatment, and spend this entire time in a planted state, their leaves will grow too tall. There are two ways to prevent excessively tall leaves. The first is to lower the temperature of the cold period in steps: start the cold period at 9°C for the first 4 to 5 weeks; then lower it to 5°C and even to 1-2°C later. This procedure will retard leaf development. Do not, however, subject the bulbs to 2 to 5°C throughout the cold period because this will result in a very long housing period and tall leaves. A second method is to leave the bulbs unplanted and maintain a constant temperature of 9°C during the cold treatment until 4 to 6 weeks before housing. At that point, plant the bulbs and continue the remaining cold treatment at 9°C to allow the bulbs to root. Leaf development will then be retarded because the root system will not be as fully developed after just 4 to 6 weeks of rooting.
Bulb size and planting density
Various bulb sizes are available for forcing purposes: 6/7, 7/8, 8/9, 9/10 and 10/+ cm. in circumference. Sizes 6/7 and 7/8 will usually produce one flower stem/bulb. Size 8/9 will produce an average of 1.5 to 2 flower stems/bulb, and sizes 9/10 and 10/+ will produce 2 to 3 flowers. For cut flower production, the smaller sizes are often preferred because harvesting more than one flower from a single bulb (when these flowers usually mature in rapid succession) is difficult. As to planting density, the bulbs are usually planted almost touching one another. Depending on bulb size, this will mean a planting density ranging from 1000 to 400/m2.
Provide sufficient water, but not too much
Plant carefully
The bulbs are usually planted in forcing boxes (containers measuring 60 x 40 cm.). A non-specific potting soil mixture similar to that used for forcing tulips, daffodils and hyacinths is also suitable for grape hyacinths. Ten percent sand is often added to the potting soil to assist proper drainage of excess water. Plant the bulbs just beneath the soil surface or with the tip of the nose just above the soil. After planting, water the bulbs and soil once thoroughly. This promotes fast uniform rooting and will produce uniform crop development. Ensure that the soil remains moist but not too wet during the cold period. If the bulbs are planted outside, make sure that the soil is properly drained and cannot dry out. Mulch with straw so that the bulbs will not freeze during the winter but can be housed later.
Sufficient light during housing
Once housed, keep the soil moist but not too wet. Wet soil increases the risk of Pythium, a soil-borne fungus that can damage the roots, and this must be prevented. Not providing enough water, however, will produce shorter plants that would be undesirable for use as cut flowers. If the bulbs are sufficiently rooted when brought into the greenhouse, a greenhouse temperature of 18°C is best. If the bulbs are not yet sufficiently rooted, the greenhouse temperature should be kept a few degrees lower to prevent flower desiccation. Provide high light intensities in the greenhouse to promote flowers with good colour. A greenhouse that provides insufficient light will result in light blue flowers.
Attractive presentation of the bunch
Harvesting takes place when a few of the individual flowers in the inflorescence are displaying good colour. Sometimes, only the flower stems are harvested and then bunched 10 to a bunch. At other times, the leaves are cut as well and included in the bunch. If the latter is the case, make sure that the flowers project above the leaves in the bunch. This may take more work but presents the product more attractively. To prevent the tops of the inflorescences from growing crookedly, always place the bunches of grape hyacinths in an upright position. If stored and transported under refrigeration, placing the bunches in water is not necessary. The product is not suitable for long storage.
Optimum production conditions prevent problems
Two fungal diseases can occur when producing grape hyacinths for pot plants and for cut flowers.
Proper production conditions and effective monitoring can help prevent many problems.
| cause | symptoms | prevention/control |
| Penicillium (a storage fungus) | During storage, a Penicillium infection is displayed as a white and later blue-green fungal weft on the bulb tunics. The fungus can penetrate the bulb through the bulb scales or the basal plate. An infection is usually found at spots where the bulb had received mechanical damage. If the fungus penetrates the bulb, the bulb tissue turns soft, grey and spreadable. Eventually, the entire bulb disintegrates. (Storage Rot) |
Avoid mechanical damage to the bulbs. Provide sufficient air circulation and keep the RH below 80-85% both during storage and when dry bulbs are receiving their cold treatment. |
| Pythium (a soil-borne fungus) | This fungus attacks the roots, resulting in the partial or entire rotting of the roots. This damage to the roots hinders water absorption and plant development. (Root Rot) |
When growing under natural conditions, grape hyacinths are not susceptible to this fungus. Excessively wet potting soil, however, can lead to an attack by Pythium. Using well-draining potting soil and avoiding overwatering will usually prevent these problems. |
A publication of: International Flower Bulb Centre P.O. Box 172 | 2180 AD Hillegom | The Netherlands t +31(0)252 62 89 60 | f +31(0)252 62 89 70 info@bulbsonline.org | www.bulbsonline.org Disclaimer The International Flower Bulb Centre accepts no responsibility for any adverse consequences resulting from the use of information obtained from this publication.